Poriferan Characteristics
- Multicellular, but lack true tissues
- Asymmetrical or radial symmetry
- Adults sessile suspension feeders
- Internal skeleton composed of spicules (calcium carbonate or silicon dioxide) or collagen fibers
|

Sponge spicules (Scypha sp.)
|

Sponge spicules (Spongilla sp.)
|
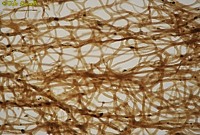
Commercial sponge collagen fibers (Spongin)
|
|
|
Class Desmospongia
Characteristics
- Includes majority of sponges
- Spicules composed of silicon dioxide or replaced by spongin (collagen network)
- Nearly all have leuconoid grade of construction
- Diverse marine and fresh water habitats
|

Fire Sponge, Tedania ignis, Belize
|

Red Encrusting Sponge, Antho sp.; Cabrillo N.M., CA
|

Red Ball Sponge, Psuedaxinella lunaecharta
|
|
|
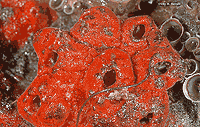
Red Sponge, probably Clathria pennata, encrusting worm tubes; La Jolla, CA
|

Red Volcano Sponge, Acarnus erithacus
|

Orange Puffball Sponge, Tethya aurantia
|

Ethereal Sponge, Dysidea etheria, collected from Florida
|

Aggregated Nipple Sponge, Polymastia sp.
|

Blue Sponge, Haliclona sp.?
|

Slippery Sponge, Aplysilla sp.?, an encrusting intertidal sponge; La Jolla, CA
|

White-tawny Fistula Sponge, Oceanapia isodictyiformis, collected from Florida
|

Finger Sponge, dried specimen
|

Elephant Ear Sponge, Ianthella sp., dried specimen
|

Sponge, possibly Gelliodes or Callyspongia sp.?, dried specimen
|

Tube Sponge, Theonella sp., dried specimen
|
|
Class Calcarea
Characteristics
- Spicules composed of calcium carbonate
- Spicules not usually differentiated into mega- vs microscleres
- Includes species with Asconoid, Synconoid, and Leuconoid body forms
- Marine
|

Scypha sp., a synconoid-type sponge; preserved specimen.
|

Leucosolenia sp., an ascanoid-type sponge; stained whole mount.
|
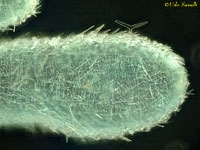
Leucosolenia sp., an ascanoid-type sponge; stained whole mount (higher magnification stacked image).
|

Pineapple Sponge, probably Sycon sp.
|

Ball Sponges, Leucandra sp.?
|
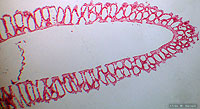
Scypha sp.; stained longitutinal section, 100x.
See also labeled photo.
|
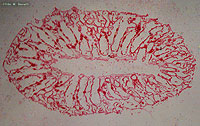
Grantia sp.; stained cross section (related to Scypha), 100x.
See also labeled photo.
|
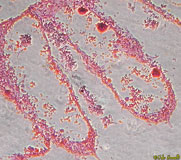
Grantia sp.; cross section showing canals and embryos, 400x.
See also labeled photo.
|
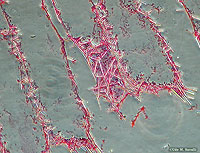
Grantia sp.; cross section showing spicules, 400x.
See also labeled photo.
|
|
Class Hexactinellida
Characteristics
- Glass Sponges
- Spicules composed of silicon dioxide, 6-rayed; complex skeletons
- Radially symmetric
- Syconoid and leuconoid body forms
- Lacks outer pinacoderm layer
- Deep water marine
|

Venus' Flower Basket, Euplectella sp., skeleton.
|
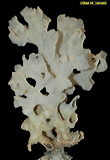
Skeleton of White Ruffle Sponge, Farrea occa?
|

Interconnected spicules forming a skeleton (Farrea sp.)
|
|
Fossil Sponges (Extinct Groups)
Characteristics
|

Archaeocyathid sponge fossil (cross sections); Early Cambrian Period, 516 Ma; Australia.
|

Model of Metaldetes, an Archaeocyathid sponge from the Cambrian Period
|

Model of Vauxia sp., a Cambrian sponge
|
|
|
































